The Is_Full output is only available if you specify an Upper Bound for a Pool A stock element that integrates and conserves flows of materials. A Pool is a more powerful version of a Reservoir (it has additional features to more easily accommodate multiple inflows and outflows).. It is a condition (False if the Pool is below the Upper Bound, and True if it is at the Upper Bound.
This output is useful because it is a special type of output called a state variable The output of an element in GoldSim whose value is computed based on the historical value of the element’s inputs (as opposed to only being a function of the current value of the element’s inputs). State variables have well-defined initial conditions. Feedback loops can only be created if they contain at least one state variable. (the primary output For an element with multiple outputs, the output that has the same name as the element. of a Pool is also a state variable). This has the important implication that inputs to the Pool (e.g., the Inflows) can reference this output without causing a recursive error.
As an example, suppose that you wanted to add water to a Pool only if it was not overflowing; once it started to overflow, you wanted the inflow rate to go to zero. To accomplish this, you could define an Expression for the Inflow as follows:
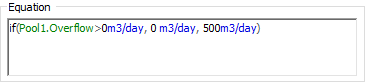
Unfortunately, because the Overflow output is not a state variable, if you then tried to link this Expression into an Inflows field for the Pool, you would get this error:
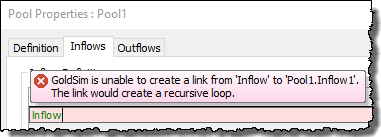
However, you can solve this problem by using the Is_Full output:
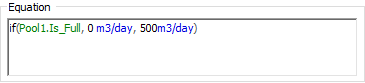
If the Expression was defined as above, then you could link to this Expression into an Inflows field for the Pool without causing a recursive error.
Learn more
- Browser View of a Pool Element
- Defining Upper and Lower Bounds for a Pool
- How a Pool Computes its Primary Output (the Quantity)
- How a Pool Computes the Individual Outflows
- How a Pool Computes the Overflow
- How a Pool Computes the Total Outflow
- Instantaneously Replacing the Current Quantity in a Pool
- Modeling Discrete Changes to a Pool
- Pool Elements
- Specifying Discrete Additions and Withdrawals to a Pool
- Specifying the Dimensions and Initial Quantity for a Pool
- Specifying the Inflow Rates for a Pool
- Specifying the Outflow Requests for a Pool
- Using the Is_Full Output of a Pool