In some models, you may want to carry out an iterative calculation at each timestep A discrete interval of time used in dynamic simulations.. This might be useful, for example, if you have a coupled system of equations that must be solved every timestep by iterating.
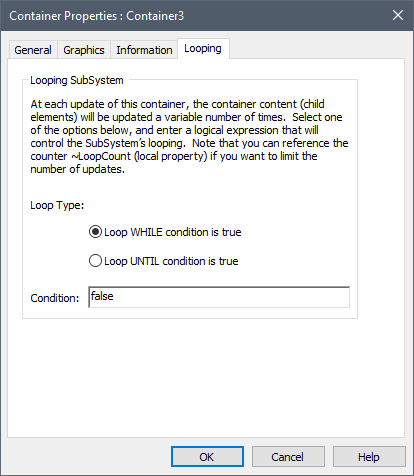
You can define a Container An element that acts like a "box" or a "folder" into which other elements can be placed. It can be used to create hierarchical models. as a looping Container by selecting the Looping Capability feature in the Container dialog. When you do so, a Looping tab is added to the Container dialog:
Looping Containers are represented in the graphics pane The primary portion of the GoldSim interface, where the graphical depiction of the model is shown. as follows:

Note: When you specify a Container as having Looping Capability, you cannot also define an Internal Clock for the Container (these two options are mutually exclusive).
Note: Looping Containers are useful when the looping calculation necessarily involves multiple elements (e.g., Reservoirs). For a calculation requiring simpler looping requirements (defining an array A collection of variables that share common output attributes and can be manipulated in GoldSim elements or input expressions., or iterating to a solution for a simple equation), a Script element would often provide a more transparent and easier solution.
Warning: When you specify a Container as a looping Container, the Treat as SubSystem feature is also automatically selected (and cannot be deselected unless you first turn off Looping Capability). That is, a looping Container, by definition, is treated as a SubSystem A specialized Container that is completely “self-contained”. SubSystems can take on some useful features and properties (e.g., conditionality, having an internal clock, and being able to loop), but also have some limitations (with regard to how they can be incorporated into feedback loops).. Because a looping Container is treated as a SubSystem, this puts certain limitations on how these Containers can be used.
Learn more
- Cloning Containers
- Container Options and Features
- Controlling Result Flags for Elements in the Container
- Controlling the Appearance of the Graphics Pane in a Container
- Copying Container Settings to Other Containers in a Model
- Influences Between Containers
- Locking a Container
- Sealing a Container
- Summary Information for a Container
- The Container Properties Dialog
- Understanding Containers
- Using Conditional Containers
- Using Looping Containers