The Triangular distribution is useful in situations where you may have little information about a value, but can provide upper and lower bounds, as well as a "best guess" or most likely value. By default, it is defined by specifying either a Minimum (0th percentile), Most Likely and Maximum (100th percentile):
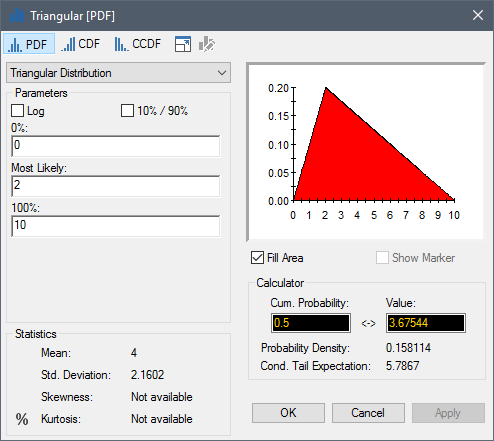
Alternatively, if you check the 10% / 90% checkbox, you can specify the 10th percentile, Most Likely and 90th percentile.
You can also specify that the logarithms of the values have a triangular distribution (by checking the Log box). In this case, all inputs to the distribution must be positive values. Note that for a Log-Triangular distribution, the Most Likely input represents the value whose logarithm is most likely. Log-Triangular distributions are often applied to quantities with large (order-of-magnitude) uncertainties.
- Beta Distribution
- BetaPERT Distribution
- Binomial Distribution
- Boolean Distribution
- Cumulative Distribution
- Discrete Distribution
- Exponential Distribution
- Externally-Defined Distribution
- Extreme Probability Distribution
- Extreme Value Distribution
- Gamma Distribution
- Generalized Beta Distribution
- Log-Normal Distribution
- Negative Binomial Distribution
- Normal Distribution
- Pareto Distribution
- Pearson Type III Distribution
- Poisson Distribution
- Sampled Results Distribution
- Student’s t Distribution
- Triangular Distribution
- Uniform Distribution
- Weibull Distribution