The Cumulative distribution is used to define custom continuous distributions. You define the distribution by specifying [cumulative probability, value] pairs. A given pair (defined by a Prob. Level and a Value) implies that the cumulative probability of the Value is equal to the specified Prob. Level:
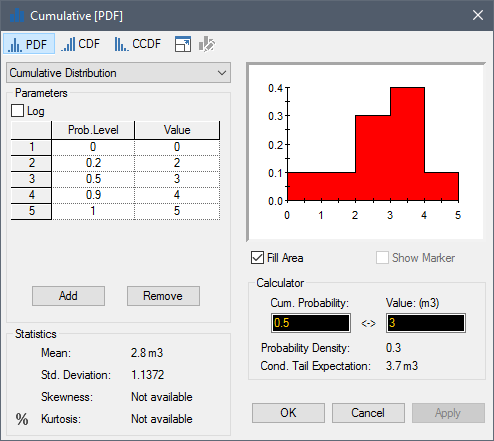
You add and remove pairs using the Add and Remove buttons (new pairs are inserted below the selected pair). In addition, if you place the cursor in the grid, the following hotkeys can be used:
| Keys | Action |
| Ctrl+Enter | creates a new row below the cursor |
| Ctrl+Shift+Enter | creates a new row above the cursor |
| Ctrl+Backspace | deletes the current row |
By definition, the first cumulative probability specified must be 0 and the last cumulative probability specified must be 1. The Prob. Level and the Value of the pairs cannot decrease as you move downward through the list. If the Prob. Levels decrease as you move down the table, GoldSim will sort the rows so that they are in increasing order when you close the dialog or press Apply. If the Values decrease as you move downward, GoldSim will warn you and ask you to fix the distribution.
Note: Specifying two or more Prob Levels with the same number results in a horizontal line in the CDF Cumulative Distribution Function. The integral of a probability density function.. Specifying two or more Values with the same number results in a vertical line in the CDF (and an infinite spike in the PDF Probability Density Function. A function whose Y-axis can be interpreted as providing the relative likelihood that the value of a random variable would be equal to value specified on the X-axis. Hence, the dimensions of the Y-axis are the inverse of those of the X-axis (i.e., the probability per unit length of the X-axis).).
You can also define the distribution as a log-cumulative (by checking the Log box). Whereas in a cumulative distribution, the density between values is constant (i.e., the distribution between values is uniform), in a log-cumulative, the density of the log of the value is constant (i.e., the distribution between values is log-uniform). If Log is checked, all Values for the distribution must be positive. Log-Cumulative distributions are often applied to quantities with large (order-of-magnitude) uncertainties.
Note: The values and cumulative probabilities must be entered as numbers and cannot be specified using links or expressions. The values are assumed to be entered in the Display Units The units (e.g., m, g, $/day) in which an output is displayed within GoldSim. for the element.
Note: You can copy and paste the entries for a Cumulative distribution from a spreadsheet. To do so, select the two columns in the spreadsheet (Probability Level and Value), and copy them to the clipboard. Then place the cursor in the upper left-hand corner of the grid (i.e., the first Probability Level) and paste (by pressing Ctrl+V).
- Beta Distribution
- BetaPERT Distribution
- Binomial Distribution
- Boolean Distribution
- Cumulative Distribution
- Discrete Distribution
- Exponential Distribution
- Externally-Defined Distribution
- Extreme Probability Distribution
- Extreme Value Distribution
- Gamma Distribution
- Generalized Beta Distribution
- Log-Normal Distribution
- Negative Binomial Distribution
- Normal Distribution
- Pareto Distribution
- Pearson Type III Distribution
- Poisson Distribution
- Sampled Results Distribution
- Student’s t Distribution
- Triangular Distribution
- Uniform Distribution
- Weibull Distribution