Once you have defined some Resources and created one or more Resource Something that has a limited supply (e.g., spare parts, fuel, skilled personnel, money) and is required in order for elements of the modeled system to carry out certain actions. Stores, you can specify ways in which elements in your model interact with those Resource Stores.
Elements can interact with a Resource Store Stockpiles or places where a Resource (e.g., parts, personnel) is stored or located when not being used. Resource Stores can be thought of as having physical locations in the system you are modeling. The can be global or local (associated with a Container). in three different ways:
- An element can Spend (consume) a Resource from the Store.
- An element can Borrow a Resource from the Store for a particular amount of time and then return it.
- An element can Deposit (generate) a Resource into a Store.
These interactions can be discrete or continuous in nature. As a result, there are actually five different kinds of possible Resource interactions:
- You can Spend a discrete amount of a Resource;
- You can Borrow a discrete amount of a Resource;
- You can Deposit a discrete amount of a Resource;
- You can Spend a Resource at a specified rate; and
- You can Deposit a Resource at a specified rate.
Only certain kinds of elements in GoldSim can interact with Resources, and not all five types of interactions may be available to a particular element.
Whenever an element does interact with a Resource Store, it does so through a Resources... button:
Depending on the context, this button is either available on the main dialog for the element or within a Trigger dialog for the element. When you press the button, the following dialog is displayed:
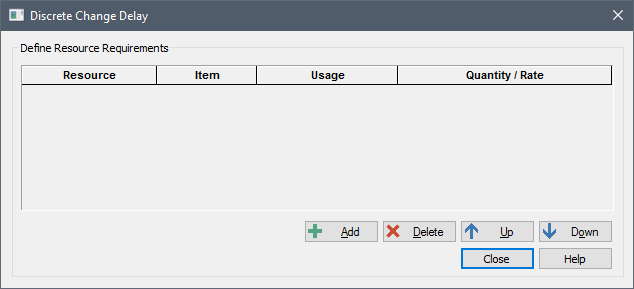
A Resource Requirement (or more generally, an interaction) is created by pressing the Add button. When you do this, GoldSim will add a row to the table of Resource Requirements:
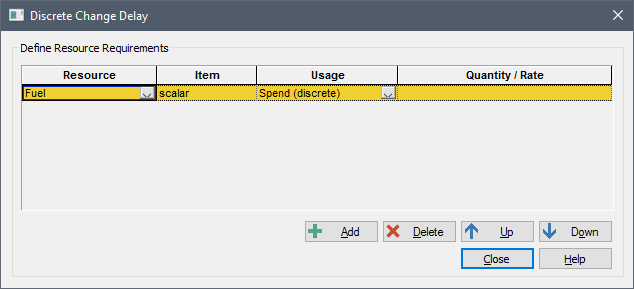
You must then edit the row to define the Resource Requirement. The Resource column is a drop-list that contains all Resource Stores that are available to the element.
What Stores are available to an element is a function of where the element is located in the model and the defined hierarchy of Local and Global Stores. The following rules are applied:
- An element can only interact with Resource Stores that are above it or at the same level within its Container An element that acts like a "box" or a "folder" into which other elements can be placed. It can be used to create hierarchical models. path. For example, if the element is located within Container1/Container2 (i.e., Container2 which is inside Container1), the element can only interact with Local Stores associated with Container1 or Container2, and Global Stores. The element would not be able to interact with any Local Stores associated with Container3 (a Container that was at a parallel level to Container1).
- If a Resource Type has multiple Stores within a particular Container path, the element can only access the Store that is closest to it. For example, if the element is located within Container1/Container2 (i.e., Container2 which is inside Container1), and Container1 and Container2 have Local Stores of a particular Resource Type, and there is also a Global Store of that Type, the element can only access the Store in Container2, even if that Store becomes empty during the simulation. If the Store in Container2 was deleted, it could then only access the Store in Container1. Only if the Store in Container1 was also deleted could it access the Global Store.
In some cases, if one Resource Store is exhausted, you may want to move Resources from another Store. This can be done, but you must manually program how and when this takes place.
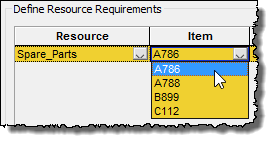
The Item column is not editable if the Resource is a scalar An output consisting of a single value or condition.. However, if it is a vector A one-dimensional array., the column provides a drop-list for you to select the item from the vector for which the Resource Requirement is defined:
The Usage column specifies the type of interaction (e.g., Spend, Borrow, etc.). As noted above, there are five possible types of interactions, but depending on the element type and the Resource Type, not all of these will be available (e.g., a Spend Rate is not available for Resource Types that are discrete items).
The Quantity/Rate column is an input field in which you specify a value that is appropriate for the particular type of Usage (e.g., discrete usages require quantities, continuous usages require rates). You can enter a value or an expression (or links to other elements). It can also be a function of time. However, the dimensions An output attribute for an element that defines the dimensionality (in terms of Length, Time and other fundamental dimensions) of the output. must be consistent with the specified Resource Type. Within this field, you can also reference several locally available properties pertaining to the amount of Resource that is available, or has been spent or borrowed.
Note: If a Resource becomes exhausted (due to Spend Rate) between scheduled updates (timesteps), GoldSim will insert an unscheduled update to accurately capture this. If you have disabled unscheduled updates Timesteps that are inserted automatically by GoldSim during a simulation and are not directly specified by the user prior to running the model. (an advanced timestepping option), such that GoldSim cannot insert an unscheduled update when the Resource becomes exhausted, a fatal error will be displayed.
A Resource Requirement can be removed by pressing the Delete button. The Up and Down buttons move Resource Requirements up and down the list (this is simply cosmetic; the order in which they are listed has no impact).
Note: If you have multiple Resource Requirements, they are only applied when they can all be met. For example, if you had a Spend requirement of 3 of PartB and 2 of PartC, and the Stores had enough of PartB, but not of PartC, neither PartB or PartC would be consumed (until both were available in sufficient quantities). In addition, all Spend requirements must first be met before any Deposit interactions are carried out.
Note: You can create multiple Resource interactions for the same Resource Store. For example, you might want to Borrow a certain quantity, and Consume (Spend) a different quantity.
The types of elements that can interact with Resources are
summarized in the first