The failure modes types available for both the Function and Action elements are described below.
Note that most failure modes are defined relative to a
Mathematical details of the failure modes are provided in
- Cumulative. For this
failure mode, you define a custom failure distribution by specifying a table of
the (cumulative) failure mode control variable value and the probability of
surviving. The dialog for defining this table is accessed via an
Edit... button, and looks like this:
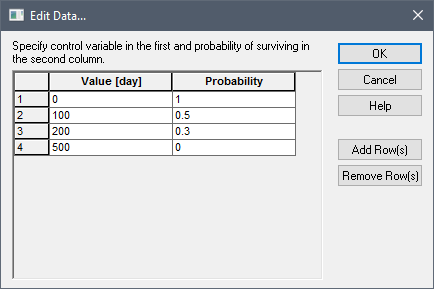
The table can only be defined using numbers (it does not accept expressions or links to other elements). You add and delete rows using the Add Row(s) and Remove Row(s) buttons.
Note: Probabilities must decrease monotonically as time increases.
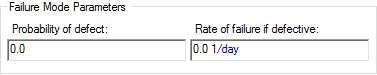
- Defective Component. For
this failure mode, you specify the probability that the component will be
susceptible to the mode, and the (Poisson) failure rate if it is susceptible. As
its name implies, it is used to simulate (typically rapid) failure due to a
small fraction of defective components.
- Erlang
multi-failure. This failure mode is used to represent the failure of a
number of identical sub-components, each of which fails according to the same
Poisson failure rate, and is used to simulate a system that has N-1 spare parts,
that are replaced immediately.
It is assumed that the first sub-component operates until it fails, at which time it is replaced by the second identical second sub-component, and so on until they have all failed. When all sub-components have failed, the component is assumed to have failed.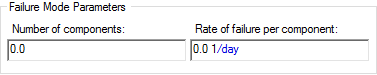
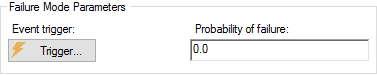
- Event-triggered failure.
For this failure mode, you specify a trigger (via a triggering dialog) and the
probability of failing whenever the triggering event occurs:
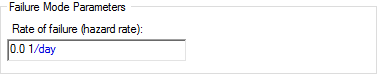
- Exponential/Poisson. This
is identical to the default failure mode if the Failure Mode tab is not
used. You define an exponential failure distribution by specifying the
rate of failure (also referred to as the hazard rate) with respect to the
failure mode control variable:
- LogNormal. For this
failure mode, you define a log-normal failure distribution with respect to the
failure mode control variable. Two LogNormal failure mode types are
provided. This allows you to define the distribution in terms of either a
Geometric Mean and Geometric Standard Deviation The square root of the variance of a distribution. The variance is the second moment of the distribution and reflects the amount of spread or dispersion in the distribution.:
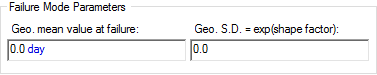
or an arithmetic Mean and Standard Deviation: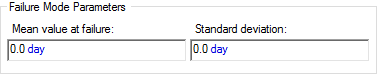
- Normal. For this
failure mode, you define a normal failure distribution with respect to the
failure mode control variable. To do so, you specify a Mean and Standard
Deviation:
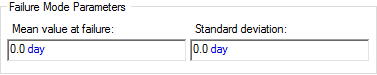
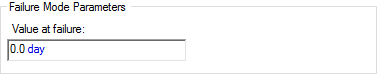
- Specified Value Exceeded.
For this failure mode, you specify the value for the failure mode control
variable which results in failure if it is exceeded:
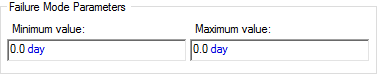
- Uniform. For this failure
mode, you define a uniform failure distribution with respect to the failure mode
control variable. To do so, you specify a Minimum value (lower bound) and
a Maximum value (upper bound):
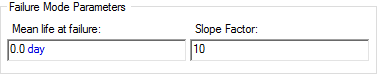
- Weibull. For this failure
mode, you define a Weibull failure distribution with respect to the failure mode
control variable. Two Weibull failure mode types are provided. This
allows you to define the distribution in terms of either a Mean life and Slope
factor:
or a Characteristic life and Slope factor: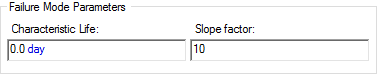
Note: The input fields for Failure Mode Parameters can accept numbers, expressions and links from other GoldSim elements. They can also be specified as functions of time. Depending on the failure mode type, however, parameters that are defined as a function of time may not change instantaneously (i.e., they may only change when the mode is repaired or the component replaced).
There are two additional failure mode types that are used to model preventive maintenance.
Learn more
- Adding Failure Modes
- Changing Failure Mode Parameters Dynamically
- Failure Mode Control Variables
- Failure Modes and Internal Requirements
- Failure Modes Available for Function and Action Elements
- Failure Modes Available Only for Action Elements
- Importing Failure Mode Information from Spreadsheets
- Modeling Coupled and Non-Fatal Failure Modes
- Modeling the Repair of Failure Modes
- The Failure Modes Tab