Feedback loops are present in one form or another in most real-world systems. There are two basic kinds of feedback loops: positive feedback loops and negative feedback loops.
- Positive feedback loops are self-reinforcing. They generate growth and amplify changes. The more adult rabbits you have, the more baby rabbits that are produced; the more baby rabbits that are produced, the more adult rabbits you have, and so on until the world is full of rabbits (or this positive loop is counteracted by a negative feedback loop A looping system in which the variables in the loop represent a closed chain of cause and effect. Note that the terms “feedback” and “cause and effect” intentionally imply that the relationship between the variables is dynamic and the system changes over time (although systems with feedback loops can also reach a dynamic equilibrium). Feedback loops contain at least one state variable.).
- Negative feedback loops are self-correcting. They drive systems toward equilibrium and balance. The more rabbits you have, the less food you have; the less food you have, the less rabbits you have.
The dynamics of most systems are driven by the interactions of many such loops.
The example below shows two simple feedback loops: the positive feedback loop associated with earning interest on a bank account; and the negative feedback loop associated with leakage from a pond. Note that both loops contain a dynamic element (in this case, a Reservoir A stock element that integrates and conserves flows of materials.):
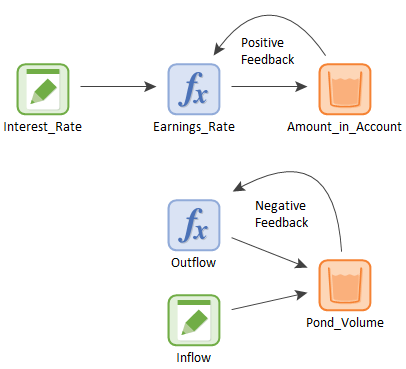
This model (Feedback.gsm) can be found in the General Examples folder of your GoldSim directory (accessed by selecting File | Open Example... from the main menu).