Timed Event An element that generates discrete event signals based on a specified rate of occurrence. elements produce discrete event signals based on a specified rate of occurrence.

The properties dialog for a Timed Event looks like this:
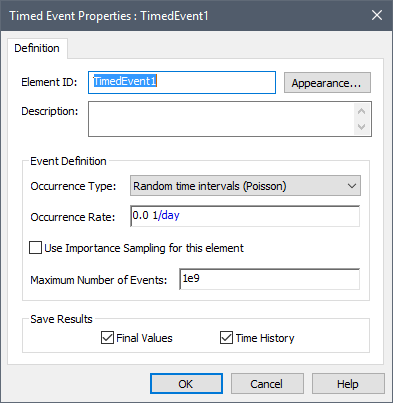
The first item that must be specified for a Timed Event is the Type.
The Type list box contains five choices:
Regular time intervals. The event occurs exactly according to the specified Rate. Hence, if the rate was 0.5 day-1, the event would occur exactly every two days, starting at two days. The Rate must have dimensions An output attribute for an element that defines the dimensionality (in terms of Length, Time and other fundamental dimensions) of the output. of inverse time. If desired, you can specify the rate as a function of time such that it changes during the simulation.
Random time intervals (Poisson). The event is simulated as a Poisson process, such that the expected number of occurrences over some time period T is equal to the product of the Rate and T. The mathematics of a Poisson process are discussed in more detail in Appendix B of the GoldSim User’s Guide. The Rate must have dimensions of inverse time. If desired, you can specify the rate as a function of time such that it changes during the simulation.
Stochastic element time intervals.
For this event, a Stochastic element
must be specified (rather than a Rate). The Stochastic element An element that can be used to quantitatively represent the uncertainty in a model input. that is specified
represents the distribution of the time intervals between events. As such,
it must have dimensions of time.The Distribution output of the Stochastic must
be referenced: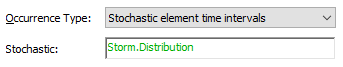
Note: if the Stochastic is time-dependent, GoldSim uses the distribution from the previous timestep A discrete interval of time used in dynamic simulations. to compute the occurrence of the next event.
Defined cumulative event count. This event requires as input a cumulative Count. This represents the cumulative number of events to be emitted. It is generally entered as an expression or a link from another element (e.g., a Time Series). It must increase monotonically (it cannot decrease with time). If the Count increases by more than one at any given time, the element will release multiple events simultaneously.
Remaining time to event. This event requires as input a Remaining time. This represents the time until the next event. This event type is designed to provide a straightforward way to insert events at specific times in the middle of a scheduled timestep. Every time the model is updated (e.g., every timestep), GoldSim recomputes Remaining time and reschedules the event. That is, this event is reset every timestep. Hence, for the event to occur, at some point the Remaining time value should be less than the scheduled timestep length (If the Remaining time was defined as a constant value that was greater than the timestep length, the event would never occur.) As an example, you could use this type of event to accurately represent when a vehicle reached a particular destination by defining the Remaining time as Distance_Remaining/Velocity.
To facilitate these type of analyses, GoldSim allows you to utilize an importance sampling algorithm to modify the conventional Monte Carlo approach so that the high-consequence, low-probability events are sampled with an enhanced frequency. That is, importance sampling serves to increase the rate of occurrence of the event. During the analysis of the results that are generated, the biasing effects of the importance sampling are reversed. The result is high-resolution development of the high-consequence, low-probability "tails" of the consequences (resulting from low-probability events), without paying a high computational price.
Importance sampling for Timed Events is specified by selecting the checkbox for Use Importance Sampling for this element. The algorithm that is used is discussed in detail in Appendix B of the GoldSim User’s Guide.
Five points regarding importance sampling of events should be noted:
- Importance sampling can only be applied if the Occurrence Type is “Random time intervals (Poisson)” or “Stochastic element time intervals”.
- Importance sampling is only applied to the first occurrence of the event. The increased sampling frequency is not applied to subsequent occurrences within the same realization A single model run within a Monte Carlo simulation. It represents one possible path the system could follow through time..
- Importance sampling of events should only be used for events that are rare. As used here, “rare” indicates an event that would not adequately be represented without enhanced sampling. As a general rule of thumb, an event will be adequately sampled if the product of the number of realizations and the expected number of events over the course of a single realization is at least 10 (this would indicate that the event would be expected to occur at least 10 times if that many realizations were executed). For example, if the rate of occurrence of an event was once every thousand years, and the simulation was run for 10 years, one could expect 0.01 events per realization. If 100 realizations were run, the total expected number of events (over all realizations) would therefore be 1. This is a rare event and importance sampling should be applied (or more realizations should be run).
- There is a limit to the effectiveness of importance sampling for extremely rare events, such that in some cases, it may become necessary to increase the number of realizations in order to effectively represent the event. In particular, the degree of biasing for low probability events that GoldSim can provide is (at most) equal to the number of realizations. For example, if the rate of occurrence of an event was once every 100,000 hours, and the simulation was run for 10 hours, one could expect 1e-4 events per realization. If 100 realizations were run, the total expected number of events (over all realizations) would therefore be 0.01. This is a rare event and importance sampling should be applied. However, importance sampling could only increase the total number of events (over all realizations) by a factor of 100 (the number of realizations) to 1 (which would still provide inadequate representation). If 1000 realizations were run, the total expected number of events (over all realizations) without importance sampling would be 0.1, but importance sampling would improve it by a factor of 1000.
- You should use importance sampling sparingly (i.e., only for those elements that really need it). This is because, as stated above, the degree of biasing for low probability failures that GoldSim can provide is at most equal to the number of realizations, and the actual biasing provided decreases with the number of elements for which importance sampling is applied.
The importance sampling algorithm is discussed in detail in Appendix B of the GoldSim User’s Guide.
With the exception of the Defined cumulative event count event type, you can specify a Maximum Number of Events to limit the total number of events that are generated.
Timed Event elements have the ability to influence when a model is updated. Typically, a model is updated at every “scheduled” timestep. That is, all the elements are computed at every timestep. A Timed Event, however, can force a model to be updated between “scheduled” timesteps.
For example, suppose that you have specified a 10 day timestep. If a Timed Event occurred at, say 23 days, GoldSim would insert an update (an “internal” event) between timesteps (i.e., at 23 days) in order to more accurately represent the event.
Note: Timed Event elements with a Defined cumulative event count do not influence when the model is updated.
Note: Timed Events are designed to interrupt the clock and insert a new update. If you choose to disable unscheduled updates Timesteps that are inserted automatically by GoldSim during a simulation and are not directly specified by the user prior to running the model., the events will be deferred to the next scheduled update.
Timed Events have up to two inputs (a Rate, a Stochastic, a Count, or a Remaining time, along with the Maximum Number of Events).
Timed Events have two outputs: 1) the discrete event signal A discrete signal indicating that something (e.g., an accident, an earthquake, a bank deposit) has occurred. itself (the primary output For an element with multiple outputs, the output that has the same name as the element.); and 2) the EventCount (i.e., the cumulative number of events which have been emitted during the realization).
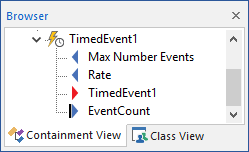
The discrete event signal output itself cannot be saved or viewed as a result.
Note: Element inputs and outputs are only shown in the browser An alternative view of a GoldSim model, in which elements are displayed in a tree, and organized either hierarchically, or by type. if you choose to Show Element Subitems (accessed via the browser context menu by right-clicking in the browser).
The example model TimedTriggered.gsm in the General Examples/Events folder of your GoldSim directory (accessed by selecting File | Open Example... from the main menu) contains an example of the use of Timed Event elements.