The properties dialog for a Material Delay A delay element that delays flows of materials (e.g., masses, volumes, items). element looks like this:
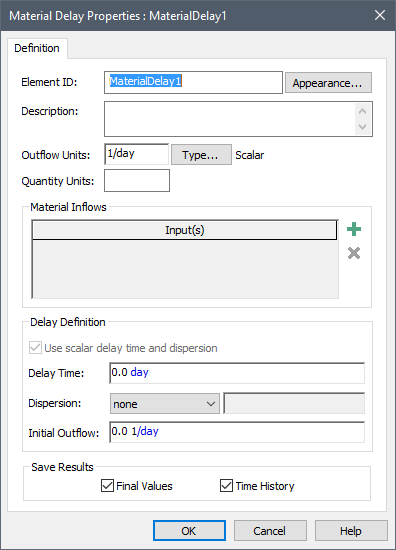
Within the Material Delay properties dialog, two sets of Display Units The units (e.g., m, g, $/day) in which an output is displayed within GoldSim. must be specified: the Outflow Units and the Quantity Units. The Outflow Units determine the dimensions An output attribute for an element that defines the dimensionality (in terms of Length, Time and other fundamental dimensions) of the output. of the Material Delay’s primary output For an element with multiple outputs, the output that has the same name as the element..
Note: GoldSim encourages (but does not require) you to specify Outflow Units for a Material Delay whose dimensions are consistent with a flow of materials. In particular, it expects the units to have dimensions of mass/time, volume/time, energy/time, currency/time, or 1/time. When you first specify the Outflow Units, GoldSim will warn you if your units do not have one of these dimensions. GoldSim will not, however, prevent you from using other units.
The primary output (the Outflow) can only be specified as a value, but can be specified as a scalar An output consisting of a single value or condition., a vector A one-dimensional array. or a matrix A two-dimensional array.. You can specify whether the Material Delay is a scalar, vector or matrix by pressing the Type... button. By default, the output of a new Material Delay element is a scalar, dimensionless value. You can also use Material Delay elements A class of elements that simulate processes that delay continuous or discrete signals and flows. The output of a delay element lags its inputs. to operate on and create vectors and matrices.
The Quantity Units determine the Display Units for the secondary output For an element with multiple outputs, an output that has a different name than the element. of the element, the Amount_in_Transit. The dimensions of this output must be the same as those of the Outflow multiplied by Time. For example, if the Outflow Units have dimensions of Mass/Time, the Quantity Units must have dimensions of Mass.
A Material Delay can have multiple Inflows. You add an Inflow to the element by pressing the Add Material Inflow button (the green +). A browser An alternative view of a GoldSim model, in which elements are displayed in a tree, and organized either hierarchically, or by type. tree showing all of the elements in the model will be displayed.
Note that this tree is organized by containment in the same manner as the main browser. To insert a link from this dialog, you select a specific output object (or an element having a primary output), and then press OK. If you press Cancel, GoldSim will insert a new blank item. In either case, the dialog will close and the item will be added to the list of Inflows in the properties dialog for the element:
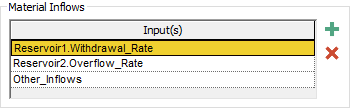
The Inflows must have the same attributes (order and dimensions) as the primary output (the Outflow). Although you can edit any of the input fields after the Inflow is added, the Inflows must all be single links to another element (i.e., you cannot enter an expression here). In addition, the Inflows must be non-negative.
Inflows can be deleted using the Remove Material Inflow button (the red X).
The Initial Outflow to the Material Delay must have the same attributes (order and dimension) as the Outflow.
Note: The Initial Outflow must be a number or a link from a static variable (e.g., a constant Data element An input element intended to represent constant inputs in a model. or a Stochastic).
The Delay Time must have dimensions of time and must be positive.
Note: The Delay Time for a Material Delay must be greater than or equal to the timestep A discrete interval of time used in dynamic simulations.. That is, GoldSim cannot delay a signal for a smaller time period than a timestep. If you enter a Delay Time which is less than a timestep, GoldSim internally treats the Delay Time as being equal to a timestep. Delay Times that are less than zero will result in a fatal error.
The Dispersion drop-list provides three choices: “None” (the default), “Erlang n”, and “Std. Deviation”.
If one of the latter two is selected, you must enter a value that quantifies the degree of dispersion to the right of this field. If “Erlang n” is selected, you must enter a dimensionless value greater than or equal to 1. If “Std. Deviation” is selected, you must enter a value with dimensions of time. The value must be greater than or equal to zero and less than or equal to the Delay Time.
If the Material Delay is specified as being an array A collection of variables that share common output attributes and can be manipulated in GoldSim elements or input expressions. (i.e., a vector or a matrix), you can specify whether the Delay Time and Dispersion are defined as scalars (with the same value being applied to all items of the array), or as arrays (with different values applied to each item of the array). This is done via the Use scalar delay time and dispersion checkbox. If this box is checked (the default), the Delay Time and Dispersion must be entered as scalars. If the box is cleared (which is only possible if the element is specified as an array), the Delay Time and Dispersion must be entered as arrays.
- Browser View of a Material Delay Element
- Material Delay Elements
- Material Delays with Time-Variable Delay Times
- Mathematics of Material Delays
- Modeling Material Delays with Dispersion
- Modeling Material Delays without Dispersion
- Representing a Material Delay with an Inflow Limit
- Specifying Initial Outflows for Material Delays
- Specifying the Inputs to a Material Delay
- Using Material Delays to Close Feedback Loops and Model Recirculating Systems