In many cases, a material flow is dispersed, “smoothed” or “smeared” such that the output represents a weighted average of previous values for the input signal. (With no dispersion, the weight for the input value at t – Delay Time is one, and all other previous inputs have a weight of zero).
To specify that the material is dispersed, you must select either “Erlang n” or “Std. Deviation” from the Dispersion drop-list. These are two alternative ways to quantify the degree of dispersion while the flow traverses the delay.
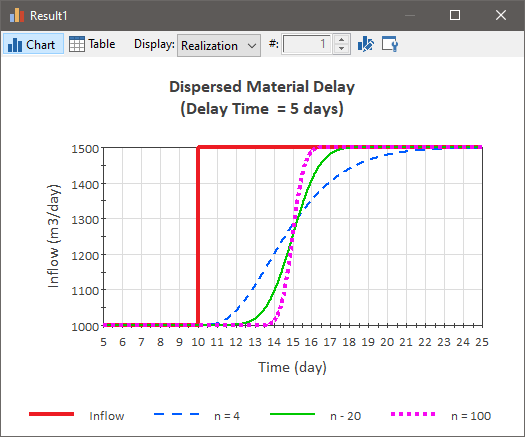
If the “Erlang n” is selected, you must enter a dimensionless value greater than or equal to 4. As n increases, the degree of dispersion decreases. As n goes to infinity, the dispersion goes to zero. The maximum amount of dispersion allowed is represented by n = 4.
If “Std. Deviation” is selected, you must enter a value with dimensions An output attribute for an element that defines the dimensionality (in terms of Length, Time and other fundamental dimensions) of the output. of time. The value must be greater than or equal to zero and less than or equal to the half of the Delay Time. As the Std. Deviation decreases, the degree of dispersion decreases. When the Std. Deviation goes to zero, the dispersion goes to zero. The maximum amount of dispersion allowed is represented by Std. Deviation = 0.5 * Delay Time.
The Erlang n and the Std. Deviation are related by the following equation:
The figure below shows the response of a Material Delay A delay element that delays flows of materials (e.g., masses, volumes, items). to a step function at ten days for various values of n:
Learn more
- Browser View of a Material Delay Element
- Material Delay Elements
- Material Delays with Time-Variable Delay Times
- Mathematics of Material Delays
- Modeling Material Delays with Dispersion
- Modeling Material Delays without Dispersion
- Representing a Material Delay with an Inflow Limit
- Specifying Initial Outflows for Material Delays
- Specifying the Inputs to a Material Delay
- Using Material Delays to Close Feedback Loops and Model Recirculating Systems