The GoldSim Contaminant Transport Module allows you to
simulate the transport of mass through an environmental system by providing a
number of specialized GoldSim elements. The most important of these is the
Transport pathways represent physical components through
which contaminant species The chemical (or non-chemical, such as bacterial or viral) constituents that are stored and transported through an environmental system in a contaminant transport model. In GoldSim, the Species element defines all of the contaminant species being simulated (and their properties). can move and/or be stored,
such as aquifers, lakes, sediments, surface soil compartments, and the
atmosphere. You define the properties of the pathways, such as their
geometry and which environmental media Materials (such as water, sand, clay, air) that constitute (are contained within) transport pathways. GoldSim provides two types of elements for defining media: Fluids and Solids. (e.g., water, soil, air) they
contain. All pathways contain one or more
You create an environmental system by defining a network of transport pathways, as shown below:
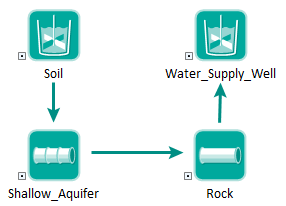
To create such a network, individual pathways are connected
via
Note: The Contaminant Transport Module relies heavily on GoldSim's ability to create and manipulate vectors. Therefore, in order to use the module, you must be comfortable with using vectors in GoldSim.
Two major types of mass flux links and three special
purpose mass flux links can be defined in GoldSim. In an
Note: The Contaminant Transport Module is a mass transport model, not a flow model. That is, it does not directly solve for the movement of media through the environmental system being modeled. Hence, you must directly enter the media flow rates associated with an advective flux link (or provide GoldSim with the equations for computing them).
Based on the properties of each pathway, the media in each pathway, the species, and the specified mass flux links, GoldSim computes the temporally varying concentrations in each pathway's media, as well as the mass fluxes between pathways. Hence, the fundamental output of a pathway element is a series of vectors:
- the mass (of each species) in the pathway;
- the concentration (of each species) within each environmental medium in the pathway; and
- the mass transport rate (of each species) to each of the pathways to which it is connected via mass flux links.
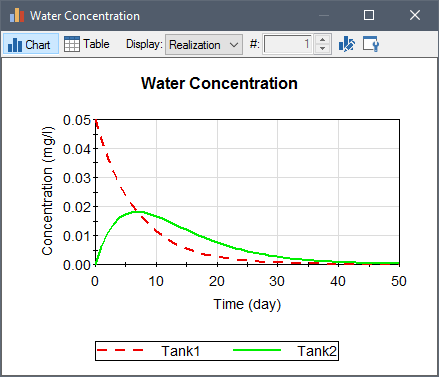
A typical pathway output is shown below: