The
objective of many contaminant transport studies is to not only compute
contaminant concentrations or flux rates at various locations in the
environment, but to also compute the impact of these contaminants on specific
This is typically done by multiplying contaminant
concentrations in environmental media Materials (such as water, sand, clay, air) that constitute (are contained within) transport pathways. GoldSim provides two types of elements for defining media: Fluids and Solids. (e.g., water, soil, air) by
user-defined
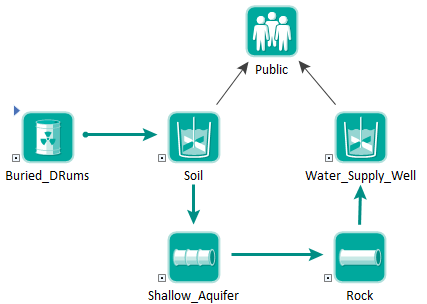
GoldSim allows you to define specific receptors, and associate these with various pathways in your environmental system. The total impact to a receptor is then computed as the sum of the impacts associated with each pathway through which the receptor is exposed to the contaminant (e.g., drinking water from a well, breathing dust in the atmosphere, ingesting soil).
Impacts may be calculated as:
- ratios of contaminant concentrations to permissible limits (i.e., hazard quotients);
- health (e.g., cancer) risks; or
- radioactive doses.