The objective of many contaminant transport calculations is to not only compute contaminant concentrations or flux rates at various locations in the environment, but to also compute the impact of these contaminants on specific receptors (e.g., humans, wildlife, flora).
Impacts may be calculated as:
- ratios of contaminant concentrations to permissible limits (i.e., hazard quotients);
- health (e.g., cancer) risks; or
- radioactive doses.
Impacts such as these are typically computed by multiplying
the concentrations in an environmental medium to which the receptor A group (usually of people) that could potentially receive impacts from contaminants in the environment. In GoldSim, a Receptor is an element that converts contaminant concentrations in the environment to impacts to a receptor group. is exposed (e.g., water in a well) by a
set of
Note: Computing the impact to a receptor always involves carrying out a term-by-term multiplication of a concentration vector A one-dimensional array. and an impact conversion factor vector. You can carry out a term-by-term multiplication of two vectors using the * operator.
Within GoldSim, you could compute an impact by using an Expression element A function element that produces a single output by calculating user-specified mathematical expressions. to carry out a term-by-term multiplication of the species concentration vector for a particular medium in a pathway by a vector of impact conversion factors. For convenience, the Contaminant Transport Module provides a specialized version of an Expression element (a Receptor element) to facilitate this calculation:

The dialog for this element looks like this:
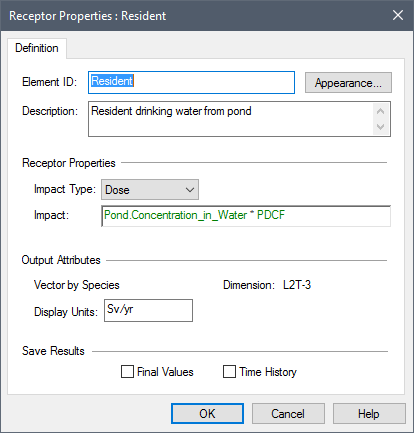
The Impact Type determines the dimensions of the impact which is computed. The equation computing the impact is entered directly below the type. The output of this equation must be a vector by species, with the dimensions being consistent with the specified impact type.
Typically, the impact to a receptor will be a sum of several term-by-term vector multiplications, since the receptor is likely to interact with multiple contaminated media Materials (such as water, sand, clay, air) that constitute (are contained within) transport pathways. GoldSim provides two types of elements for defining media: Fluids and Solids. (e.g., water in a well, soil, dust).