Pipe pathways are intended to represent environmental features that behave as fluid conduits, such as aquifers, rivers, channels and pipelines:

An Aquifer pathway A transport pathway element that is intended to represent a feature that essentially behaves as a fluid conduit. Internally, an Aquifer pathway actually performs its computations by creating a temporary set of linked Cell elements during the simulation. actually performs its computations by creating a temporary set of linked Cell elements during the simulation, which are subsequently removed at the end of the simulation.
The properties dialog looks like this:
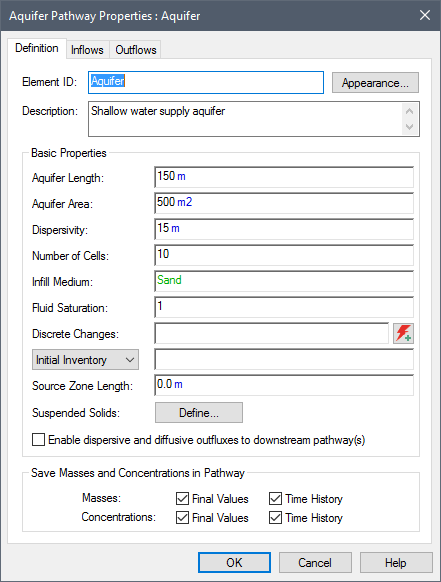
The Fluid flowing through the Aquifer pathway is always the Reference Fluid A special type of Fluid element that provides a basis for defining partition coefficients between media for the various species in the model (i.e., the ratio of the species’ concentration in the medium to its concentration in the Reference Fluid at equilibrium).. The geometry of the pathway is defined by specifying an Aquifer Length and an Aquifer Area. You must also define the Number of Cells to be used to discretize the system. Based on this, GoldSim internally creates a series of linked Cell pathways. The specified Infill Medium and Fluid Saturation are used to determine the quantity of media Materials (such as water, sand, clay, air) that constitute (are contained within) transport pathways. GoldSim provides two types of elements for defining media: Fluids and Solids. in each Cell. A pathway Dispersivity is also specified. Advective and diffusive flux links are automatically created by GoldSim to appropriately model advection, dispersion and diffusion through the linked Cells.
The output of an Aquifer pathway element consists of the total mass of each species The chemical (or non-chemical, such as bacterial or viral) constituents that are stored and transported through an environmental system in a contaminant transport model. In GoldSim, the Species element defines all of the contaminant species being simulated (and their properties). in the pathway, and the concentration of each species in the flowing Reference Fluid exiting the pathway (i.e., in the last Cell).