When modeling an aging chain consisting of specific age groups (e.g., 0 to 1 years, 1 to 2 years, etc.), it is often most appropriate to model the chain using a series of Material Delay elements.
Each Delay has a fixed delay time (with no dispersion) corresponding to the age cohort (e.g., 1 year). As such, the residence time in the cohort does not represent an average; it is an exact time required to "transit" the cohort. The structure of the model would typically look something like this:
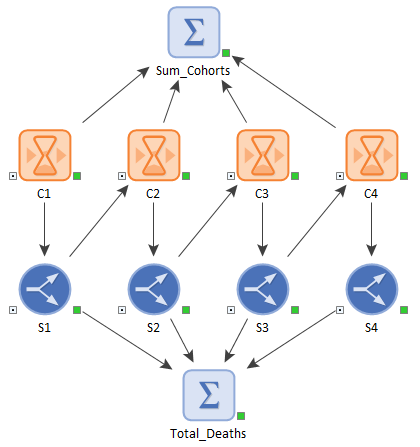
Note that each Delay does not flow into the next Delay in the series. Rather, it flows through a Splitter An element that splits an incoming signal between a number of outputs based on specified fractions or amounts. Typically, the signal will be a flow of material (e.g., water), but it could also be a resource, or a discrete transaction., so that losses (e.g., due to deaths) can be accounted for prior to graduating to the next cohort. Of course, there could also be additional flows into and out of a cohort (due to immigration and emigration). The Material Delay A delay element that delays flows of materials (e.g., masses, volumes, items). dialog for a typical cohort for this simple would look like this:
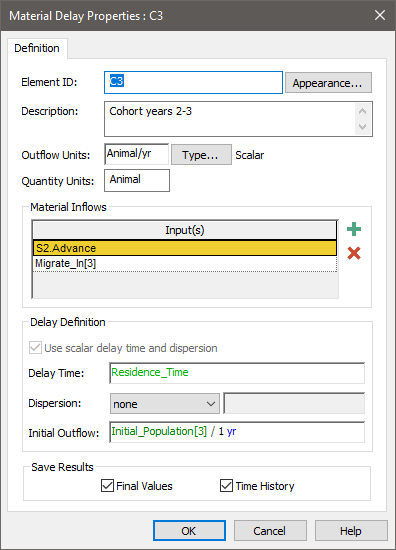
An example file which illustrate how aging chains can be modeled using a series of Material Delays (AgingChain.gsm) can be found in the General Examples folder in your GoldSim directory (accessed by selecting File | Open Example... from the main menu).