GoldSim allows you to specify that suspended Solids are present in the Aquifer. These Solids are assumed to be advected and dispersed along the Aquifer. Species The chemical (or non-chemical, such as bacterial or viral) constituents that are stored and transported through an environmental system in a contaminant transport model. In GoldSim, the Species element defines all of the contaminant species being simulated (and their properties). which partition onto the suspended Solids are transported with them as they move through the Pipe.
Suspended solids are specified to be present in the Aquifer via the Suspended Solids... button on the Aquifer dialog. When you press this button, the following dialog is displayed:
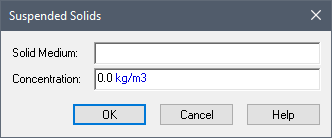
An Aquifer can have a single suspended Solid for which you must define the Solid Medium and the Concentration:
Solid Medium: This is the solid suspended in the Aquifer. It must be a previously defined Solid medium.
Concentration: This is the concentration of the suspended solid in the Aquifer fluid. It has dimensions An output attribute for an element that defines the dimensionality (in terms of Length, Time and other fundamental dimensions) of the output. of mass per volume.
Suspended solids in an Aquifer can increase the "carrying capacity" of the pathway fluid, by allowing solute species to sorb onto and be transported by particulates. This has the effect of reducing retardation due to sorption onto infill material. Mathematically, suspended solids in an Aquifer can be thought of as increasing the effective concentration in the pathway fluid, thereby increasing the mass flux of species out of the Aquifer. In particular, assuming no dispersion, the advective mass rate of species i leaving the Aquifer, Ratei, becomes:
Ratei = Q cdi (1 + Ki Vsusp csusp)
where Q is the flow rate in the Aquifer (volume/time), cdi is the dissolved concentration of species i (mass/volume), Ki is the partition coefficient for species i for the suspended solid medium (volume/mass), csusp is the suspended solid concentration (mass/volume), and Vsusp is the dimensionless Advective Velocity Multiplier for the suspended Solid (a property of the Solid).
Note: The suspended solid concentration only impacts advective mass flux links leaving the Aquifer and does not have any impact on the diffusion of particulates into the Aquifer. That is, if a diffusive mass flux link A mass flux link in which species diffuse between pathways according to a concentration gradient. is created between a Cell containing a suspended solid and an Aquifer containing the same suspended solid, for the purpose of simulating the diffusive flux of particulates, the concentration of particulates on the Aquifer side of the link is assumed to be zero.
- Aquifer Pathway Example: Advection, Retardation and Dispersion
- Aquifer Pathway Outputs
- Comparing Pipes and Aquifers
- Computing Pipe and Aquifer Pathway Concentrations Accounting for Transverse Dispersion
- Defining Basic Aquifer Properties
- Features and Capabilities of Aquifers
- Flux Links to/from Aquifers
- Saving Results for an Aquifer
- Simulating Discrete Changes to the Mass Inventory in an Aquifer
- Simulating Suspended Solids in an Aquifer
- Understanding How an Aquifer Pathway Works
- Viewing an Aquifer in the Browser