When an advective mass flux link A mass flux link in which a quantity of a medium is specified to flow from one pathway to another, carrying dissolved, sorbed, and/or suspended species with it. is created, GoldSim creates several new inputs and outputs on the two linked pathways which subsequently appear in the browser An alternative view of a GoldSim model, in which elements are displayed in a tree, and organized either hierarchically, or by type. view and interfaces for these pathways.
On the "from" or "outflow" pathway (the pathway from which the medium is flowing):
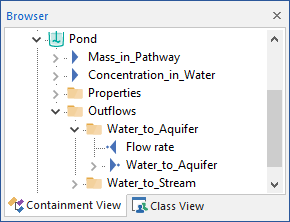
- GoldSim creates a new output named Medium_to_Path2, where Medium is the name of the flowing medium, and Path2 is the name of the linked pathway (toward which the medium is flowing). For example, if Water was flowing from a pathway named Aquifer to a pathway named Pond, GoldSim would create a new output on the Aquifer pathway called Water_to_Pond. Like all GoldSim outputs, when the output appears in an expression, the name of the element is included prior to the output name (Aquifer.Water_to_Pond). This output represents the mass flux itself, and is a vector A one-dimensional array. by species The chemical (or non-chemical, such as bacterial or viral) constituents that are stored and transported through an environmental system in a contaminant transport model. In GoldSim, the Species element defines all of the contaminant species being simulated (and their properties). with dimension of mass/time.
- GoldSim creates a new input named Flow rate. This is the flow rate in the link. It has dimensions An output attribute for an element that defines the dimensionality (in terms of Length, Time and other fundamental dimensions) of the output. of volume/time for fluids and mass/time for solids.
These new items are organized under a "folder" within the browser view of the element called Outflows:
On the "to" or "inflow" pathway (the pathway to which the fluid is flowing):
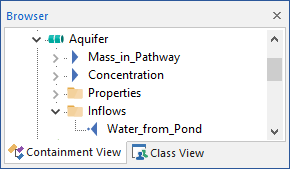
- GoldSim creates a new input named Medium_from_Path1, where Medium is the name of the flowing medium, and Path1 is the name of the linked pathway (from which the medium is flowing). For example, if Water was flowing from a pathway named Aquifer to a pathway named Pond, GoldSim would create a new input on the Pond pathway called Water_from_Aquifer. This input represents the mass flux itself, and is a vector by species with dimension of mass/time.
This new item is organized under a "folder" within the browser view of the element called Inflows:
These new items in the browser views of the pathways are useful because they can be used in conjunction with the Link Cursor A special cursor for creating links invoked by double-clicking on an input or output object in a browser. to create links. For example, rather than editing the flow rate in the link using the editing dialog, you could create a link to Flow rate using the Link Cursor. Similarly, you could link the mass flux output itself into an Expression element A function element that produces a single output by calculating user-specified mathematical expressions., a Sum element A simple function element that sums values. or an Extrema element A function element that computes the maximum value (peak) or minimum value (valley) achieved by its input during a simulation..
Note: If you create multiple advective fluxes between the same two Cells, GoldSim will append the letter "c" and a number to the end of the input and output names. For example, if a second advective flux was added from Cell Aquifer to Cell Pond, the output on the Aquifer Cell would be named "Water_to_Pondc2" and the input on the Pond Cell would be "Water_from_Aquiferc2".