The editing dialog for a Cell pathway A transport pathway element that is mathematically equivalent to a finite difference node. Cells are commonly applied to simulate discrete compartments in an environmental system (such as ponds, lakes, shallow soil compartments, or the atmosphere). is shown below:
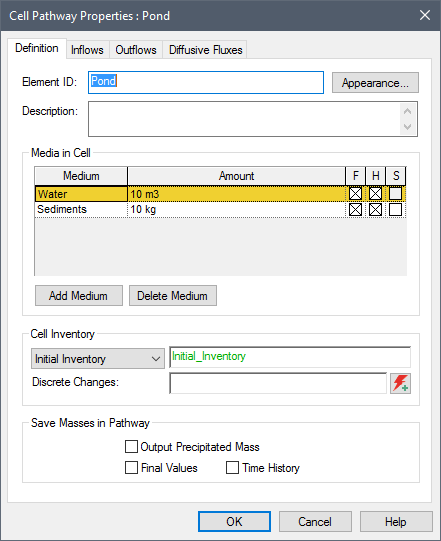
The primary input that must be defined for a Cell pathway is the quantity of each medium present in the pathway. The Reference Fluid A special type of Fluid element that provides a basis for defining partition coefficients between media for the various species in the model (i.e., the ratio of the species’ concentration in the medium to its concentration in the Reference Fluid at equilibrium). is automatically present in each Cell when it is first created. The number of additional Fluids and Solids that can be added to the Cell is unlimited, but most Cells will typically include no more than one or two additional media Materials (such as water, sand, clay, air) that constitute (are contained within) transport pathways. GoldSim provides two types of elements for defining media: Fluids and Solids..
Learn more
- Advective Flux Links to/from Cells
- Automatically Generating Cell Networks Using the CellNet Generator
- Basic Concepts of the Cell Solution Algorithm
- Cell Pathway Outputs
- Coupling a Network of Cell Pathways to a Network of Reservoir or Pool Elements
- Defining Basic Cell Properties
- Defining Initial and/or Boundary Conditions for a Cell
- Defining Suspended Solids in a Cell
- Diffusive Flux Links to/from Cells
- Direct Transfer Flux Links to/from Cells
- Features and Capabilities of Cells
- Precipitate Removal Flux Links to/from Cells
- Saving Results for a Cell
- Simulating Discrete Changes to the Mass Inventory in a Cell
- Simulating Solubility Limits in Cells
- Treatment Flux Links to/from Cells
- Viewing a Cell in the Browser