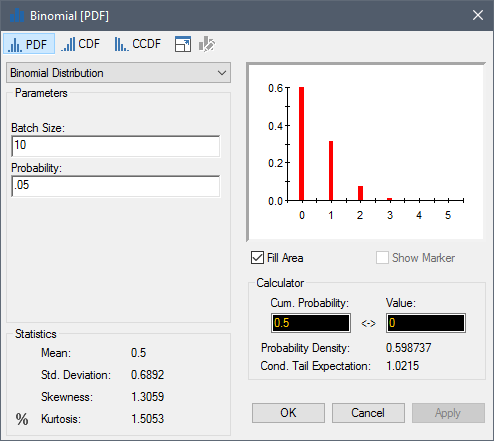
The Binomial distribution describes the probability of a certain number of instances, given a (dimensionless) batch size and a probability of occurrence. As such, by definition, a Binomial distribution is dimensionless.
For example, you could use a Binomial distribution to define a probability distribution for the number of defective widgets produced, given a particular batch size (e.g., 10) and the probability of any given widget being defective (e.g., 0.05).
It requires two inputs, the Batch Size (which should be an integer) and the Probability. Like the Poisson distribution, it is a discrete distribution containing only integer numbers.

 Note: Since this is a discrete distribution, the PDF view does not
actually display a probability density
function. Instead, it displays a probability
mass function.
Note: Since this is a discrete distribution, the PDF view does not
actually display a probability density
function. Instead, it displays a probability
mass function.